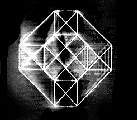
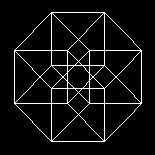
 a cube having more than three dimensions.
a cube having more than three dimensions.
One of the simplest multi-dimensional
structures is the four-dimensional
analogue
of an ordinary cube.
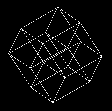 A theory of space as multi-dimensional
A theory of space as multi-dimensional
structure includes physical dimensions beyond
the three "spatial" and one "temporal"
including
gravity and other phenomena
as spatial dimensions.
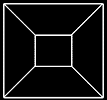
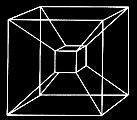
A hypercube cannot be visualized
but one can unravel a hypercube
into its lower components
of ordinary 3D cubes (tesseract)
or to visualize its shadow-projections
or cross sections
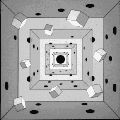 The shadow of a cube
The shadow of a cube
a square within a square.
The shadow of a hypercube
a cube within a cube.

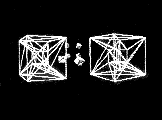
The hypercube model is used as a communication structure
in parallel computing and complex information management
 Engineers are constantly dealing with mathematical
structures using the square root of minus 1, which has a mathematical identity defining a 90 degree deviation
from "normal space", intrinsic to the mechanics of electro-magnetic
phenomena.
Mathematicians deal with multidimensional cosmology, or
hyperspace, by assigning most of the phenomena as physical dimensions, which are mutually orthogonal to each other, electric, magnetic and gravitic flux as dimensional manifestations.
Engineers are constantly dealing with mathematical
structures using the square root of minus 1, which has a mathematical identity defining a 90 degree deviation
from "normal space", intrinsic to the mechanics of electro-magnetic
phenomena.
Mathematicians deal with multidimensional cosmology, or
hyperspace, by assigning most of the phenomena as physical dimensions, which are mutually orthogonal to each other, electric, magnetic and gravitic flux as dimensional manifestations.
